Note: All blog posts on this website are 100% AI generated and has not been fact checked or edited. Do not rely on anything on this website. Instead, use it to learn about the output quality by ZimmWriter.
AIBlogPostWriter
Examples of 100% AI Written Articles by ZimmWriter
AIBlogPostWriter
Examples of 100% AI Written Articles by ZimmWriter

Cloud-Based Remote Access VPNs Explained
Cloud-based remote access VPNs represent advanced networking solutions that enable secure, encrypted connections between users and cloud-hosted resources through virtual private network gateways. These systems utilize sophisticated encryption protocols, including SSL/TLS and IPSec, while incorporating multi-factor authentication and dynamic security measures to protect data transmission. Modern cloud VPN architectures leverage distributed server networks to minimize latency, implement load balancing for optimal performance, and offer scalable deployments that adapt to organizational needs. The technology's projected market growth to $27.08 billion by 2029 reflects its increasing adoption, driven by remote work demands and enhanced cybersecurity requirements. Understanding the intricate technical components reveals the comprehensive security framework underlying these essential business tools.
The Rise of Cloud VPNs
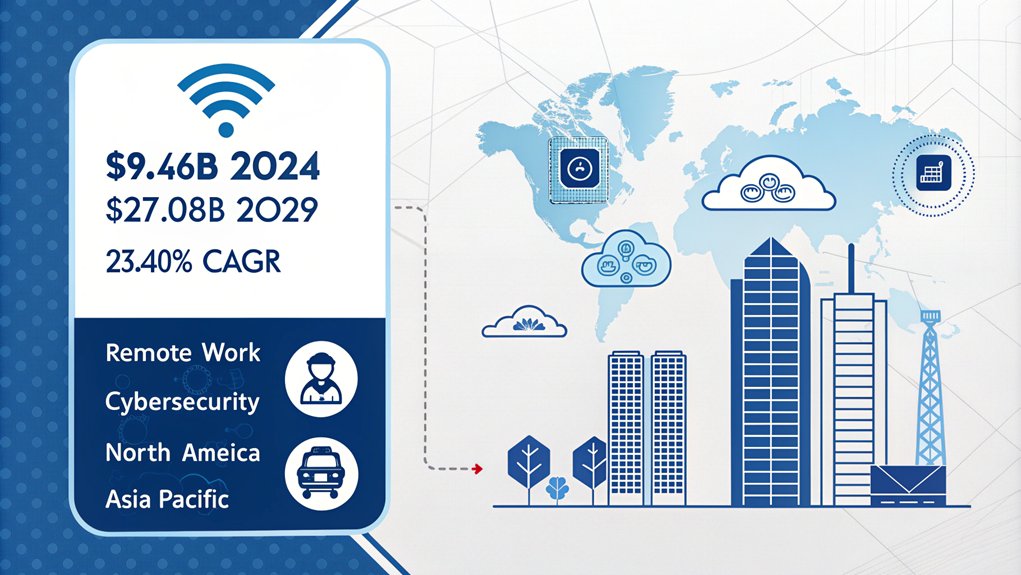
The digital security landscape has undergone a dramatic transformation with the meteoric rise of cloud-based VPN solutions. Current market projections illustrate this trajectory, with the cloud VPN sector anticipated to expand from USD 9.46 billion in 2024 to USD 27.08 billion by 2029, demonstrating a robust CAGR of 23.40%. The market is expected to reach global value projections of $137.7 billion by 2030.
This substantial growth stems from several interconnected factors, predominantly the widespread adoption of remote work policies and BYOD practices across industries. Organizations, confronting escalating cybersecurity threats and regulatory requirements, increasingly gravitate toward cloud VPN implementations to ensure secure remote access to corporate resources and maintain compliance with data protection frameworks such as GDPR. The integration of AI and machine learning is enhancing VPN capabilities and security features across platforms. Recent developments show that limited technical knowledge among employees poses challenges for widespread implementation.
The market's evolution is particularly pronounced in North America, which currently holds the dominant market share, while the Asia-Pacific region exhibits the highest growth potential. Major technology providers, including Cisco Systems, Microsoft Corporation, and Google LLC, have responded to this demand by developing sophisticated VPNaaS offerings that emphasize scalability and reliability. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this transformation, compelling organizations to rapidly deploy secure remote access solutions and catalyzing the transition from traditional on-premise infrastructure to cloud-based security architectures.
Understanding Cloud VPN Architecture
Modern cloud VPN architecture represents a sophisticated amalgamation of distributed computing resources, security protocols, and networking components that work in concert to deliver secure remote access capabilities. At its core, this architecture employs strategically positioned VPN gateways that function as intermediary nodes, facilitating encrypted data transmission between end-users and protected network resources. Remote desktop management enables seamless access to work computers from any location. Virtual infrastructure management simplifies deployment and maintenance compared to traditional hardware-based solutions. High availability configurations ensure 99.99% uptime for mission-critical operations.
The foundational infrastructure comprises multiple interconnected elements, including authentication systems, encryption modules, and dynamic routing mechanisms. These components establish secure tunnels utilizing established protocols such as IPsec or SSL/TLS, while simultaneously managing user authentication through robust multifactor verification processes.
The architecture's scalability manifests through its cloud-based deployment model, allowing organizations to expand or contract their VPN infrastructure based on operational requirements. This flexibility extends to the integration of advanced security features, including network segmentation and threat prevention mechanisms, which operate seamlessly within the cloud environment.
Through this architectural framework, enterprises can implement globally accessible yet highly secure remote access solutions that maintain consistent performance levels while reducing dependency on physical infrastructure, ultimately optimizing both operational efficiency and resource utilization.
Key Security Features
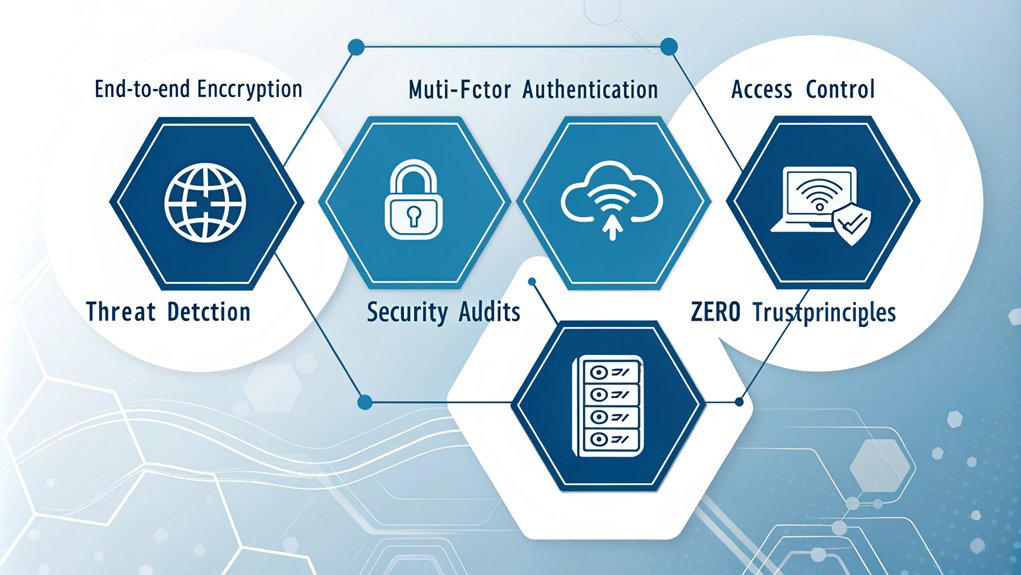
Security excellence in cloud-based remote access VPNs hinges on a comprehensive suite of protective features that work in concert to safeguard organizational data and resources. Cloud-based encryption protocols, including SSL/TLS, IPSec, and WireGuard, establish secure data transmission pathways, while end-to-end encryption ensures information integrity throughout the entire communication process. Single point control through centralized management simplifies security policy enforcement and user access administration.
Advanced access control mechanisms form a critical security cornerstone, implementing granular management protocols and robust authentication systems. Multi-factor authentication, coupled with sophisticated device validation processes, significantly enhances the verification framework, while integration with IAM tools provides comprehensive user privilege management. The implementation of no-log policies ensures user activity and browsing history remain completely private. The adoption of zero trust principles has become increasingly vital as organizations move away from traditional VPN setups.
Network security measures incorporate strategic segmentation and continuous threat detection protocols, supplemented by advanced malware protection systems. Regular security audits maintain system integrity, while strict adherence to industry compliance standards ensures regulatory alignment.
These security features address fundamental risk considerations, including credential theft prevention and misconfiguration mitigation. However, organizations must remain vigilant regarding vendor performance metrics and scalability parameters, while maintaining adequate visibility into network operations to detect potentially malicious activities within the encrypted traffic streams.
Traditional Vs Cloud VPNS
Fundamental differences between traditional and cloud-based VPNs manifest across multiple operational dimensions, including scalability, performance, and management complexity. Cloud VPNs demonstrate superior elasticity through automated deployment mechanisms, whereas traditional VPNs often necessitate manual configuration and hardware additions for expansion. Modern organizations increasingly adopt cloud VPNs due to increased interconnectivity needs. Organizations with limited IT expertise particularly benefit from hosted VPN solutions.
In terms of security architecture, cloud VPNs typically implement TLS/SSL encryption protocols and leverage sophisticated IAM solutions for authentication, while traditional VPNs rely on IPsec protocols and conventional username/password combinations. Cloud-based solutions benefit from the robust security infrastructure of established cloud service providers, though traditional systems offer greater direct control over security parameters. The perimeter-based access model of traditional VPNs increases vulnerability to potential security breaches.
Performance metrics and cost structures reveal distinct advantages in cloud implementations, particularly through geographically distributed servers that minimize latency. The pay-as-you-go model eliminates substantial upfront investments characteristic of traditional VPN deployments, while simultaneously reducing ongoing IT maintenance expenses.
Management frameworks in cloud VPNs emphasize automation and centralized control through intuitive interfaces, facilitating seamless integration with cloud-based services. Conversely, traditional VPNs require more intensive manual oversight and may present challenges when interfacing with modern cloud environments, particularly in terms of configuration complexity and maintenance requirements.
Deployment Best Practices
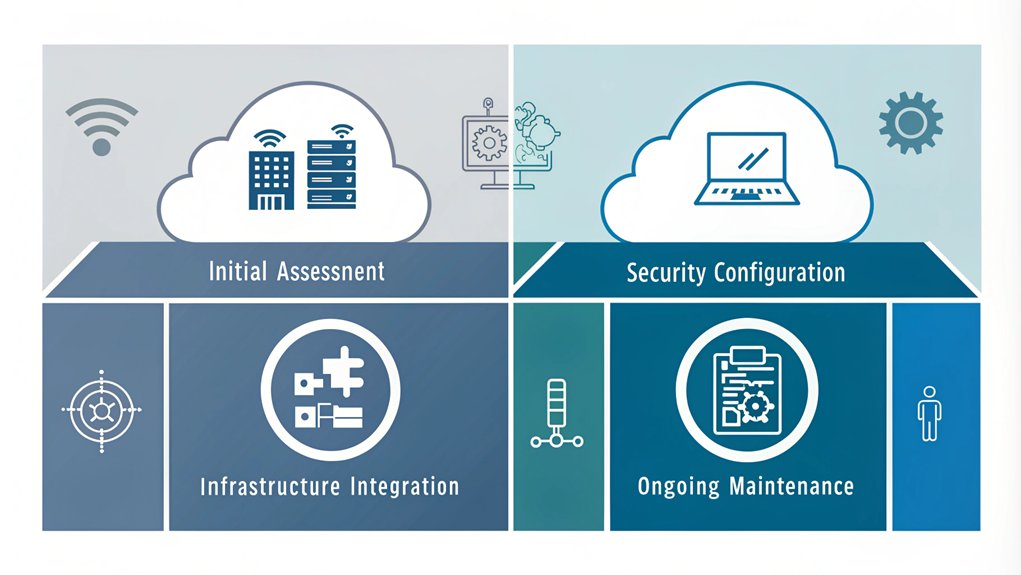
Implementing cloud-based remote access VPNs demands a methodical deployment approach to ensure optimal performance and security. Organizations must begin with a comprehensive assessment of network requirements, evaluating bandwidth capacities, security protocols, and scalability needs before selecting an appropriate cloud provider based on technical specifications and geographical presence. A thorough evaluation should include solution compatibility testing to prevent potential infrastructure issues. Resource distribution can be achieved through cost-effective methods compared to traditional on-premises solutions.
The deployment process necessitates meticulous security configuration, incorporating robust encryption protocols, multi-factor authentication mechanisms, and precisely defined firewall rules. Network architects must establish comprehensive access control lists while implementing sophisticated monitoring systems to track user behavior and detect potential security breaches. Organizations should implement split tunneling configurations to optimize network traffic flow and reduce bandwidth consumption.
Integration with existing infrastructure requires careful consideration of network topology, incorporating load balancing mechanisms and quality of service policies to optimize performance. Organizations should implement scalable architectures that can dynamically adjust to fluctuating demand patterns, while ensuring seamless connectivity between on-premises and cloud-based resources.
Sustained operational excellence depends on rigorous maintenance protocols, including regular software updates, continuous performance monitoring, and systematic security audits. Network administrators must utilize advanced monitoring tools to track performance metrics, configure alerting systems, and maintain comprehensive audit trails for compliance and security purposes.


